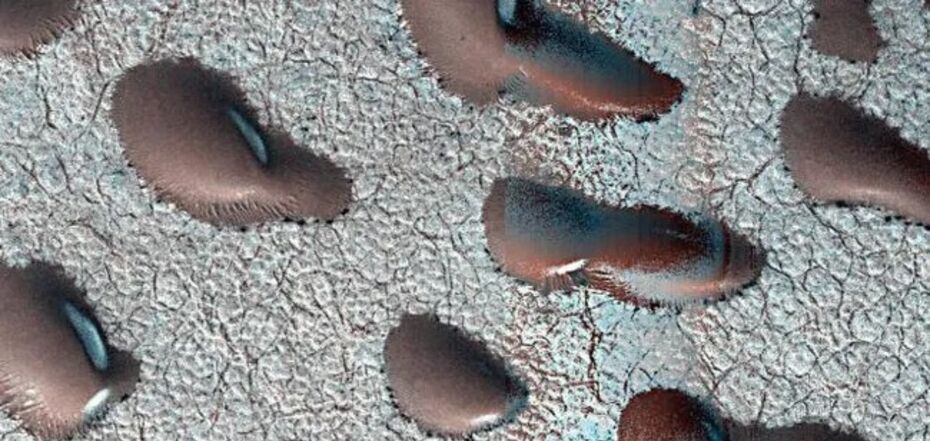
A giant “bean,” that may indicate signs of life, has been spotted on Mars. Photo
A NASA satellite spotted a giant “bean” on Mars. These strange frozen objects can be seen on the Red Planet’s dunes until spring.
The photo of the frozen dunes in the northern hemisphere of Mars was taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Scientists suggest that the study of Martian “beans” can help determine whether there was ever enough water on this planet to support life, LiveScience writes.
In the photo released by NASA, the dunes look stationary, although on Mars, as on Earth, they usually migrate when the wind picks up. However, the photo shows that the Martian dunes are covered with a layer of carbon dioxide in winter. Therefore, the frost prevents the wind from moving the dunes until the spring thaw, experts say.
However, scientists have noticed that the “beans” on Mars are covered with frost. This is likely to help researchers find out whether water once existed on the surface of the Red Planet long enough for life to exist there.
Even though frost is formed from carbon dioxide and not water, it still affects the likelihood that Mars had water for long periods in the past, scientists suggest.
According to the researchers, the amount of carbon dioxide on Mars varies depending on the angle at which the planet is located to the Sun.
It is known that the Earth wobbles a bit, rotating around a slightly tilted axis, and this gives us different seasons. But the tilt of Mars’ axis has been fluctuating greatly for millions of years, dramatically changing the seasons.
Scientists emphasize that when Mars tilts more, ice from carbon dioxide turns into gas on a large scale for the entire planet. Experts suggest that a thicker atmosphere could be enough to keep water in a liquid state for a long time.
With a better understanding of how carbon dioxide appears and disappears on Mars under current conditions, scientists can make better predictions of the past climate on Mars, experts say.
Comments (0)